Court System In India
Court system in india. The judicial system or court system is also known as the judiciary system. The constitution is the supreme source of law in India and these laws are enforced by the judicial system or these courts which are considered as the watchdog of the Indian Constitution. Ad Youve seen the news now discover the story.
Subscribe to The Economist. Articles 124 to 147 of the Constitution of India lay down the composition and jurisdiction of the Supreme Court of India. Two days after the Indian Constitution happened.
These courts have jurisdiction over a state a union territory or a group of states and union territories. It requires efficient and effective Court Management System in place. Ad Youve seen the news now discover the story.
Seven decades after independence the system of long vacations for courts is a practice introduced by the British rule in India to provide or privilege their judges ample time to travel home and back to work. Enjoy unrivalled analysis of the issues that lie behind the headlines. Trial courts and appellate courts.
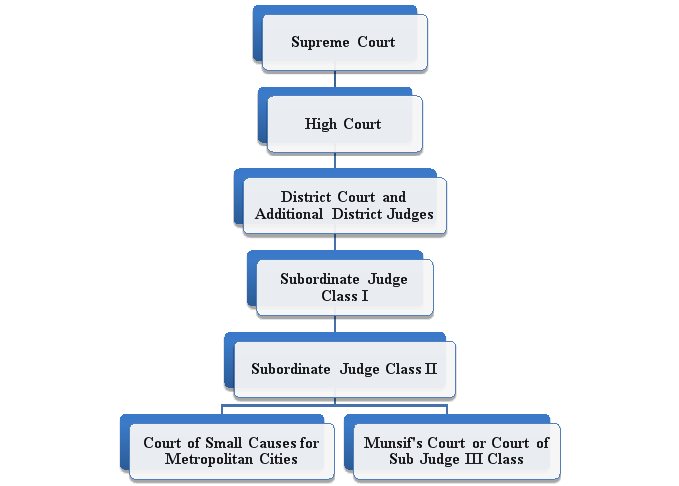
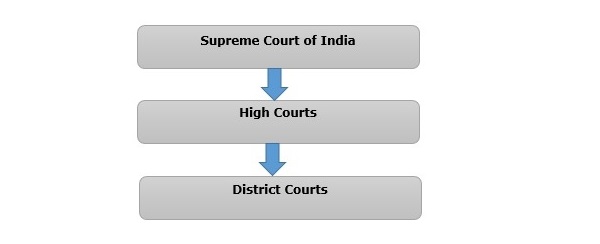
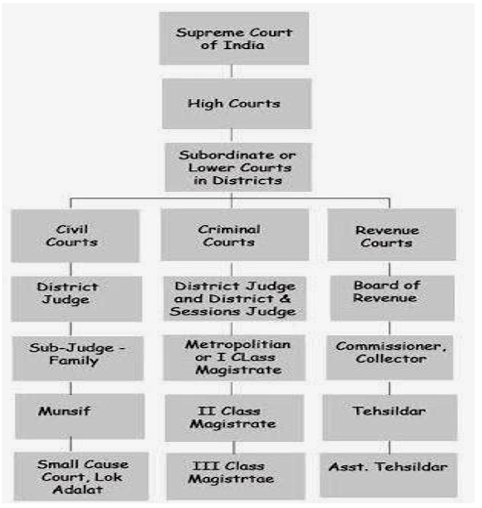
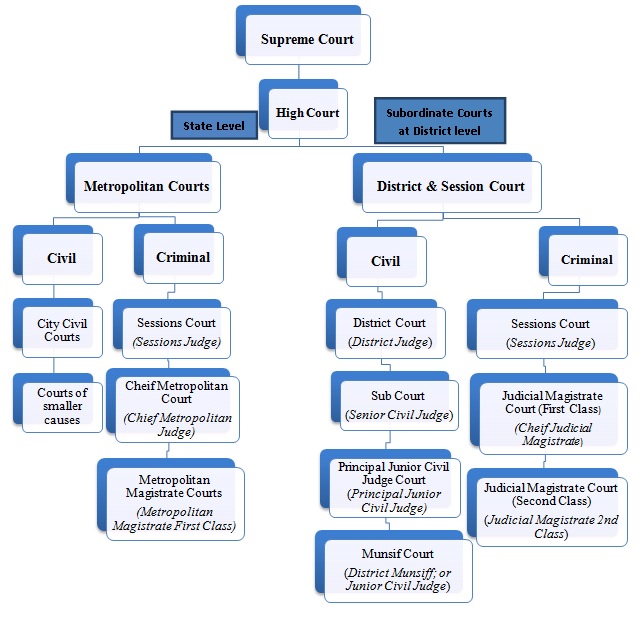
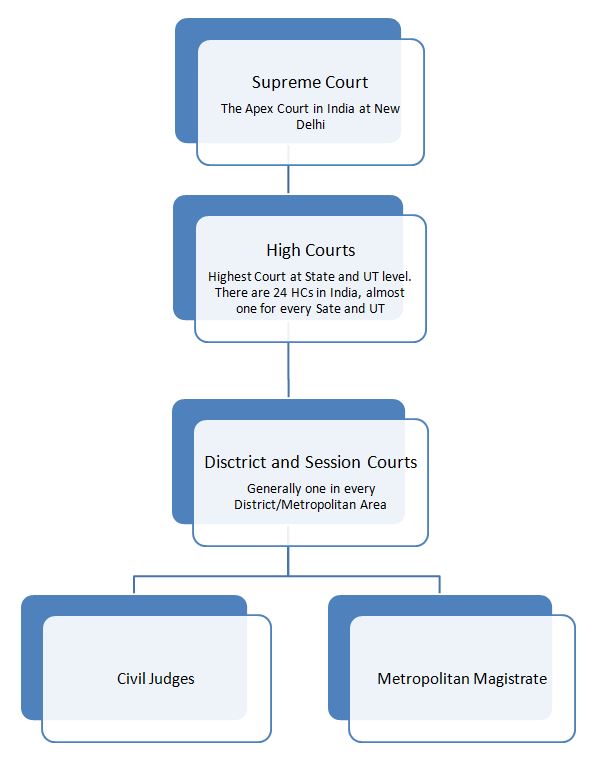
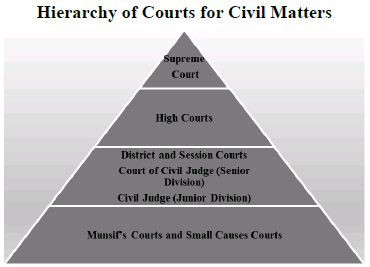
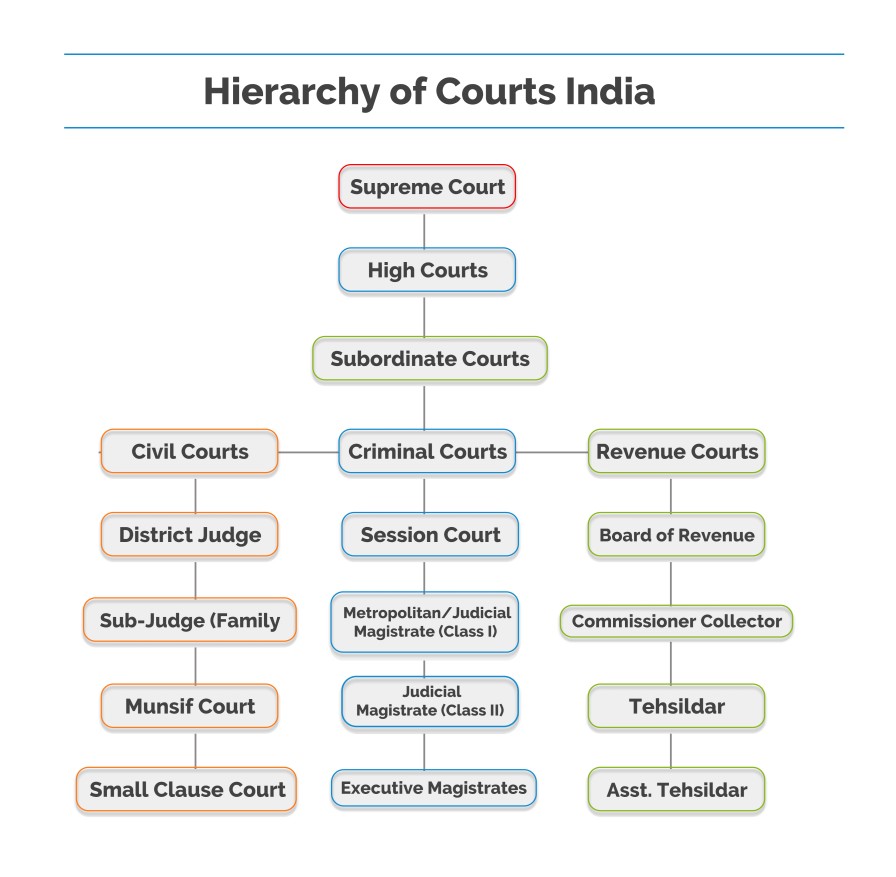
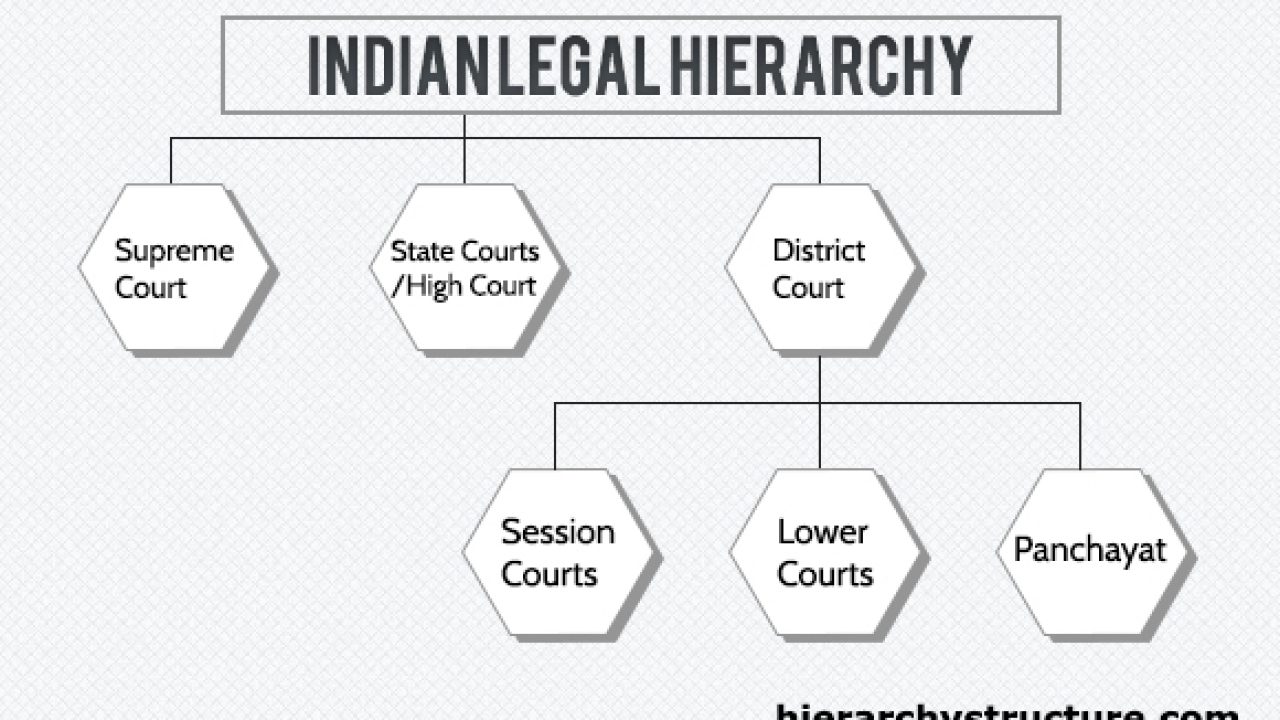
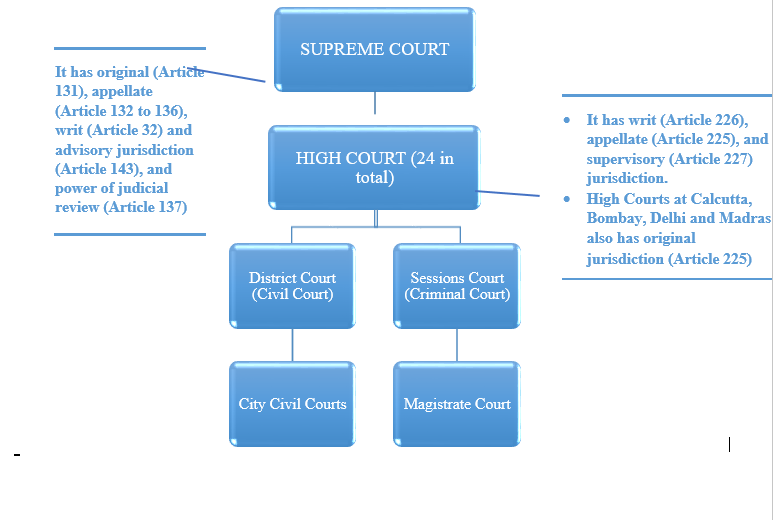
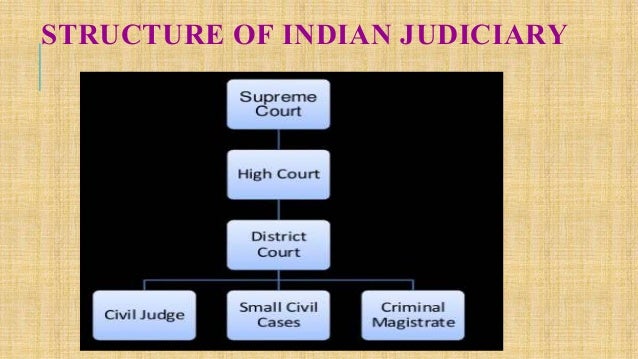
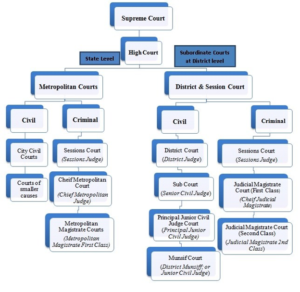
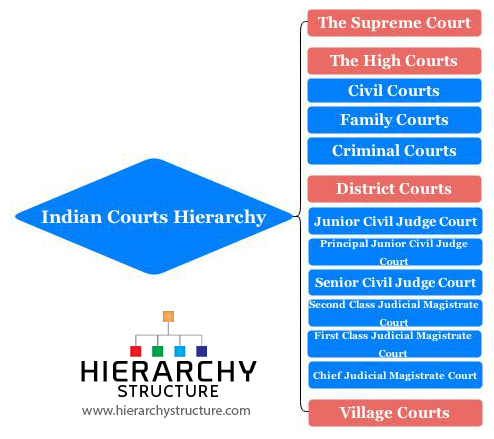
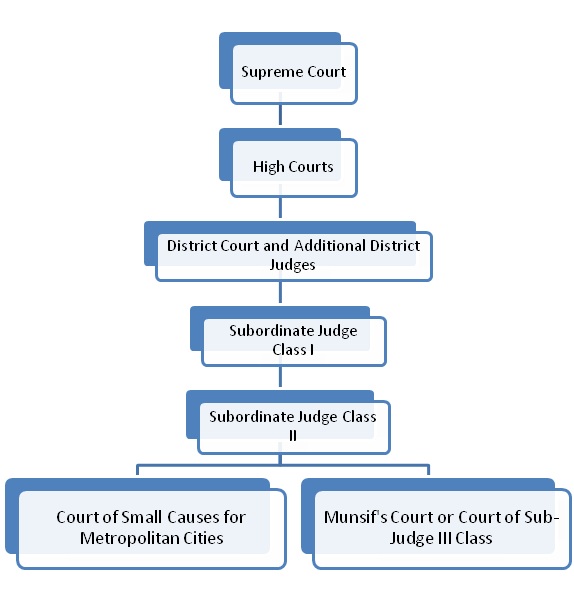
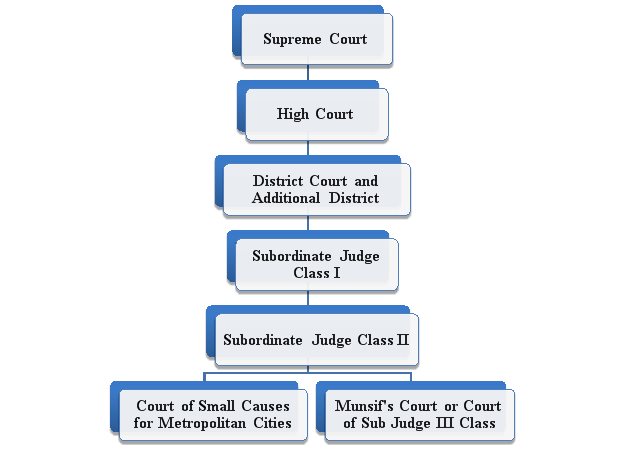
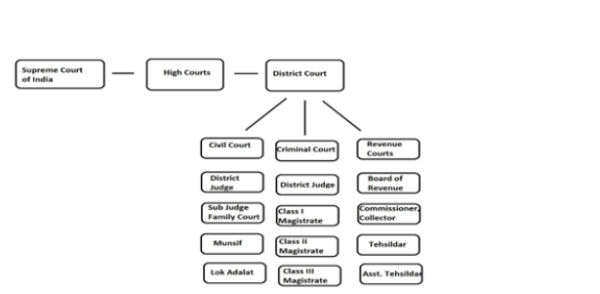
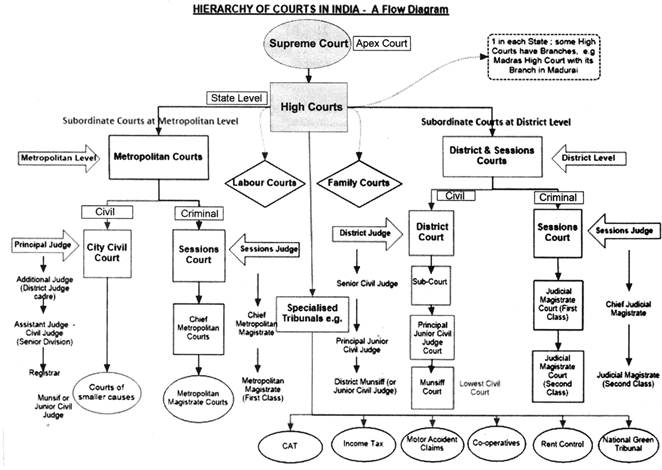
There are four types of courts in India ie Supreme Court High Court District Court and subordinate courts. The seat of the Supreme court is in New Delhi. Click here for District Court Servies.
25 High Courts There are 25 High Courts in India. Hierarchy of courts and their jurisdiction should be properly defined to deal with the disputes which arise every day in a big country like India. The Calcutta High Court established.
Each district of India has a District Court. The judicial system or judiciary consists of judges and other magistrates.
Also the ruling of the District Court is under the subject of the appellate jurisdiction of the High court.
The seat of the Supreme court is in New Delhi. Articles 124 to 147 of the Constitution of India lay down the composition and jurisdiction of the Supreme Court of India. Also the ruling of the District Court is under the subject of the appellate jurisdiction of the High court. Enjoy unrivalled analysis of the issues that lie behind the headlines. Click here for District Court Servies. The Supreme Court of India deals with the cases at the National level the High Court deals with cases at the State level and Subordinate courts Civil and Criminal deals with the cases at the District and Subordinate level. NJDG works as a monitoring tool to identify manage and reduce pendency of cases. Seven decades after independence the system of long vacations for courts is a practice introduced by the British rule in India to provide or privilege their judges ample time to travel home and back to work. Judicial system or the court system in India consist of Supreme Court Highs Courts District Courts or subordinate courts and constitutional courts.
Hierarchy of courts and their jurisdiction should be properly defined to deal with the disputes which arise every day in a big country like India. Read Also How Judges of Indian Court are appointed. 13th Finance Commission allocated Rs. The seat of the Supreme court is in New Delhi. The Supreme Court of India deals with the cases at the National level the High Court deals with cases at the State level and Subordinate courts Civil and Criminal deals with the cases at the District and Subordinate level. It consists of different levels of courts serving different functions and over 575 judicial officers hearing more than 18 million cases each year. Hierarchy of courts and their jurisdiction should be properly defined to deal with the disputes which arise every day in a big country like India.

.jpg)








.jpg)














Post a Comment for "Court System In India"